Cloud 101: A No-Fluff Guide to AWS Concepts That Matter
Investing in the cloud with AWS instead of managing your on-premise infrastructure is worth every penny for you either as an individual or business. In essence, just move to the cloud.
With AWS, you don’t play the guessing game with website traffic or worry about serving users across the globe. Any of its services you use, scales with you whether you have 10 visitors or 10 million.
You essentially use the AWS services when you need it, and pay for what you use. Kind of like electricity bill, but smarter.
In this article, we will explore the core concepts of AWS cloud, including the key benefits of the cloud, some of the foundational services you need to know, and so on.
Let’s begin this exploration!
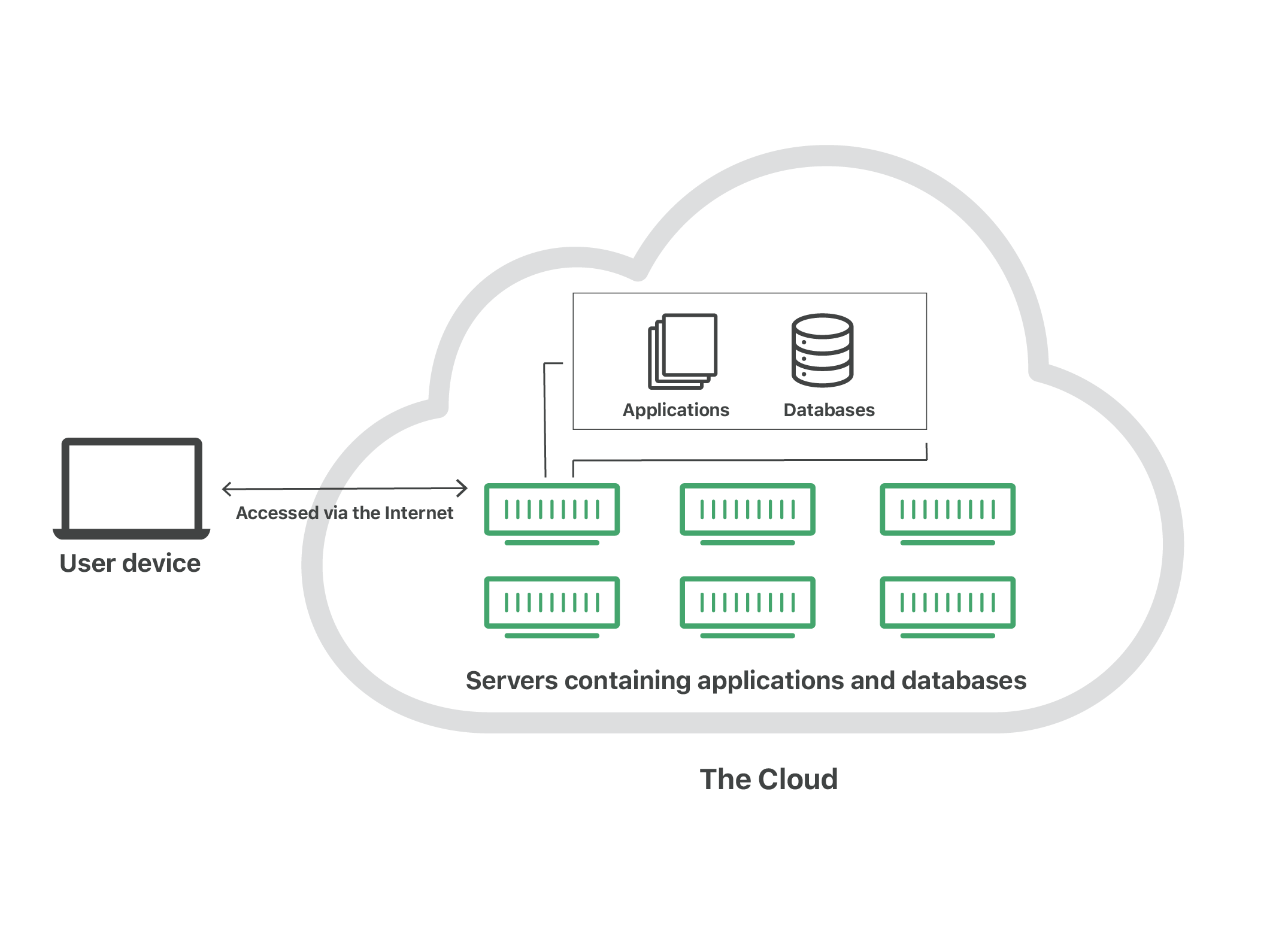
What is the Cloud?
The cloud is not mystical but a collection of distributed servers in a warehouse and other infrastructure like networking hardware, database storage, and hard drives accessible over the internet.
What are the AWS Foundational Services?
AWS has hundreds of services available but there are just a few of these tools that are foundation to everything else which are the following:
- Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2)
- Relational Database Service (RDS) and DynamoDB
- Simple Storage Service (S3)
- Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
- Identity and Access Management (IAM)

To learn more about each of these services, the AWS official documentation covers in-depth details about them.
Benefits of the Cloud
As a business, I believe you should leverage some of these benefits that makes AWS the leading cloud provider.
- Elasticity: Elasticity deals with the ability to adapt to workload changes. A typical example will be Amazon.com handling a huge spike in traffic on prime day and scales back those resources the next day to a normal load.
- Scalability: The ability to handle increased workload by adding resources like scaling up a database because the size has grown over time.
- High availability: In the event of an environment disaster, deploy your application to multiple regions. Therefore, high availability allows a system to continue functioning, even if some components fail. When a data center is down, traffic is routed to another.
- Reliability: Reliability means performing accurately and consistently whenever it is needed.
- Agility: Develop, test, and launch applications to deliver business value. With AWS, it is possible to launch a new business application in days rather than months.
Other benefits of the cloud include:
- Global reach
- Pay-as-you-go pricing
- Economies of scale
Economics of AWS
When considering to use AWS, these are the things you need to look into:
-
Total cost of ownership: Just like a car, apart from the cost, there are other cost that needs your attention like insurance, taxes and registration, repairs/maintenance, and so on which can be divided into capital (up-front) and operating (ongoing) expenses.
-
Capital expenses: The same concepts can be applied to hardware and software. Your up-front cost goes into purchasing your servers, racks, cables, software licenses, and if the servers gets old, you may need to purchase new ones over time. The beauty of AWS is that they handle all these things for you, so you don’t need to worry about the capital expenses.
-
Operational expenses: On the other hand, the operating expenses demand that you need people to maintain the servers, electricity, air conditioning, training your staff to have the latest skills, and so on. Also, some of the requirements here can be removed as well such as people required to setup and maintain the servers, electricity, air conditioning is covered by AWS in the data centers.
P.S.: The rent and subscription you pay AWS to use their service is considered as operating expenses.
Now, let’s discuss on ways to reduce costs in AWS.
Ways to Reduce Costs in AWS
- Right-sized infrastructure: Only use the infrastructure you need like the right number of machines, don’t just spin up a bunch of services. This is important to note before you gets charge uncontrollably 😭.
- Automation: Schedule start and stop time for servers that you use for development. You can also automate your billing and send notification on spend limit to save money .
- Compliance scope: Adhere to regulations based on your industry.
- Managed services: AWS provisions the underlying infrastructure, handles patching, updates, and so on allowing you to use the service without worrying about creating servers, installing software and licensing costs.
Conclusion
Understanding the concepts and fundamentals are important in guiding how you approach AWS to build smarter and scalable apps. AWS is not a service that is overwhelming to use because it gives you access to only the tools you need at any given time with a structure to monitor and pay for what you use.

